Maintaining software and databases at Bonita Springs Healthcare is crucial to ensuring system reliability, data integrity, security, and optimal performance. Proper maintenance practices also help in minimizing downtime and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations. Here’s a comprehensive approach to software and database maintenance:
Regular Software Updates and Patching
- Software Updates: Schedule regular updates for all software applications, including operating systems, to ensure they are running the latest versions. This helps in fixing bugs, improving performance, and adding new features.
- Security Patches: Apply security patches as soon as they are released to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Prioritize critical patches for software handling sensitive data.
- Automated Patch Management: Implement automated patch management tools to streamline the patching process and reduce the risk of missing critical updates.

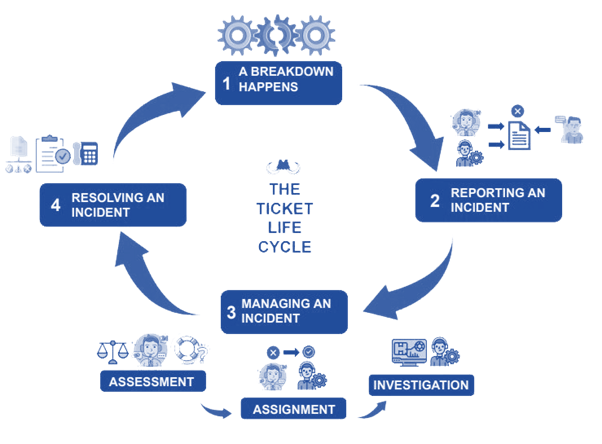
- Data Backup: Regularly back up databases to secure locations, ensuring that data can be restored in case of corruption or loss. Implement both full and incremental backups based on the criticality of the data.
- Database Optimization: Perform regular database optimization tasks such as indexing, defragmentation, and query optimization to improve performance and reduce load times.
- Database Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to keep track of database performance, identify slow queries, and detect potential issues before they affect operations.
- Data Integrity Checks: Schedule regular data integrity checks to identify and resolve any inconsistencies or corruption in the database.
- Access Control Management: Regularly review and update access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive systems and data. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) for better security.
- Encryption Maintenance: Ensure that all sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, is encrypted using strong encryption protocols. Regularly update encryption methods to adhere to current standards.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure that all software and databases comply with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA. Address any gaps or non-compliance issues promptly.
- Vendor Updates: Stay in close contact with software vendors to receive updates, patches, and support. Ensure that vendor support contracts are up to date.
- Third-Party Software Monitoring: Regularly monitor and review third-party software integrations to ensure compatibility and performance.
- Maintenance Logs: Maintain detailed logs of all maintenance activities, including software updates, patches, database optimizations, and security checks. This documentation is essential for tracking maintenance history and compliance.
- Reporting: Generate regular reports on system performance, security status, and maintenance activities. Use these reports to identify trends, address recurring issues, and plan future maintenance.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement a feedback mechanism for users and IT staff to report issues and suggest improvements. Use this feedback to refine maintenance processes and address pain points.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of the maintenance strategy to ensure it meets the evolving needs of Bonita Springs Healthcare. Adjust as necessary to incorporate new technologies or address emerging challenges.

